This Video Explains How Sound Waves Are Converted Into Sound Signals
Almost all sound waves are unique contributing to the uniqueness of each sound. When someone speaks, a telephone ring or anything else creates a different ‘sound’. Sound travels through the air in waves, which when picked up result in a series of vibrations within the ear.
The hearing is a complex process that involves many parts of the ear working together to convert sound waves into information that the brain understands and interprets as sounds. The quality of the sound depends on how well they are captured and how clearly they are sent to our brains and finally on how well our ears work.
Also Read: The Reason Why Sounds Are Being Heard From Jayalalithaa’s Tomb
Almost all sound waves are unique. That’s why each person or thing sounds different – and why one person or thing doesn’t always sound the same. Some sound waves might be high pitched or low pitched, loud or soft.
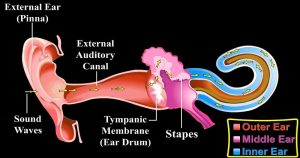
The Sections Of The Ear:
There are three major parts to the ear:
- Outer Ear: Catches the sound waves and directs them into the middle ear.
- Middle Ear: The middle ear transfers sound waves in the air into mechanical pressure waves that are then transferred to the fluids of the inner ear.
- Inner Ear (cochlea): Turns pressure waves into sound signals that our brain can understand.
How The Hearing Works:
The hearing nerve then sends the information to the brain with electrical impulses, where they are interpreted as sound. A presence of hearing loss may exist if any part of the hearing process is not functioning properly. Damage to inner hair cells can occur due to excessive noise, ear disease or degenerative conditions.
Also Read: The Reason Behind “Sound Of Victory” In Paralympic Medals
Featured Image: Source