Ebola Virus: Symptoms, Types, Treatment, and Prevention
Ebola Virus the most concerning issue these days which is panicking and creating furore across the globe. The most powerful and developed nations on this earth too worried regarding this virus outbreak which is causing the human life loss in an considerable scale and threaten to human lives on this earth with frightening results.

What is Ebola Virus?
Ebola virus which is also known as Zaire Ebola virus is one of five cognized viruses within the ‘Genus Ebola Virus’. Ebola virus disease causes severe fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals and it is similar to the four of the five known Ebola Viruses including Ebola Virus is called Ebola Virus Disease.
Transmission of Ebola Virus in Humans
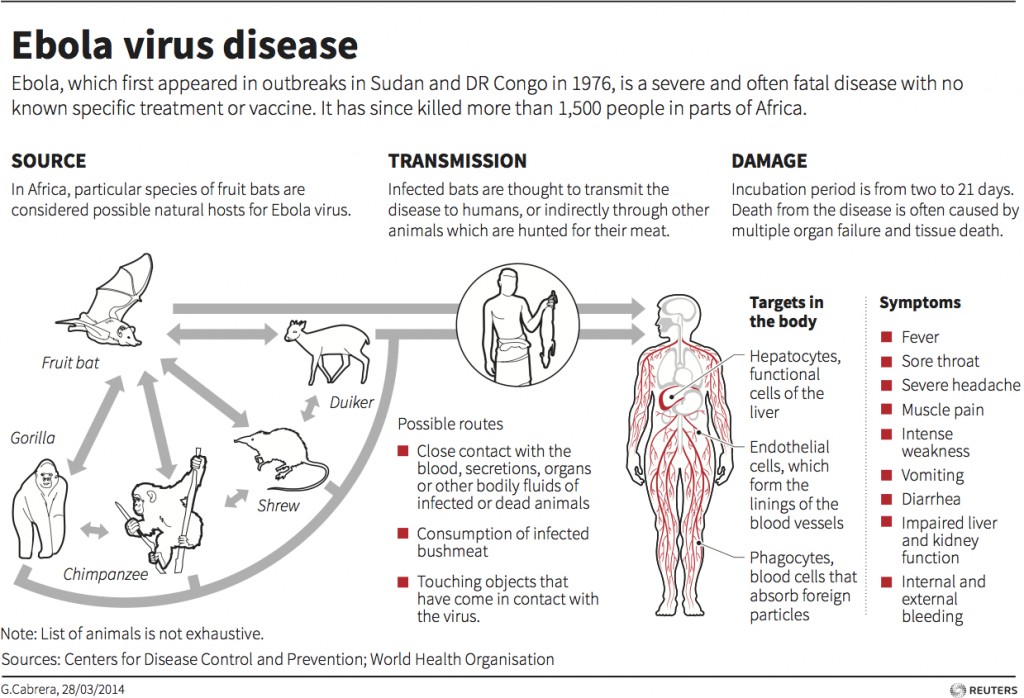
Ebola Virus is transmitted through human to human transmission from wild animals. As per the official data Ebola fatality rate is around 50% on an average. And the outbreak fatality rates have increased from 25% to 90%.
History of Ebola outbreak:
Ebola Viral disease initial outbreak occurred in remote villages in Central Africa, near tropical rain-forests while the most recent outbreak in West Africa has involved major urban as well as rural areas. The initial outbreak occurred in the year in 1976 in 2 simultaneous outbreaks, one in Nzara, Sudan, and the other in Yambuku, Democratic Republic of Congo. The latter occurred in a village near the Ebola River, from which the disease takes its name.
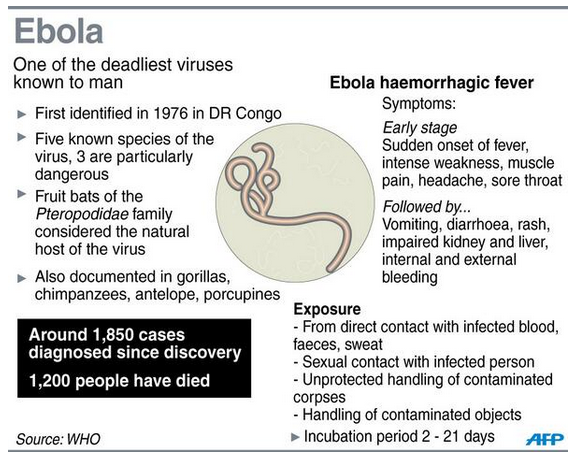
Community engagement is key to successfully controlling outbreaks. Good outbreak control relies on applying a package of interventions, namely case management, surveillance and contact tracing, a good laboratory service, safe burials and social mobilization. Early supportive care with re-hydration, symptomatic treatment improves survival. There is as yet no licensed treatment proven to neutralize the virus but a range of blood, immunological and drug therapies are under development. There are currently no licensed Ebola vaccines but 2 potential candidates are undergoing evaluation.
If we look back in to the medical records the virus family Filoviridae includes 3 genera which are Cuevavirus, Marburgvirus, and Ebola virus. And the tropical Africa has 5 species that have been identified as Zaire, Bundibugyo, Sudan, Reston and Taï Forest although the Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Zaire Ebola virus, and Sudan Ebola virus have been associated with large outbreaks in Africa. The very recent outbreak causing the 2014 west African outbreak belongs to the Zaire species.
Symptoms of Ebola Viruses:
The most occurring symptoms of Ebola Virus diseases show up 2 to 21 days after infection and usually are
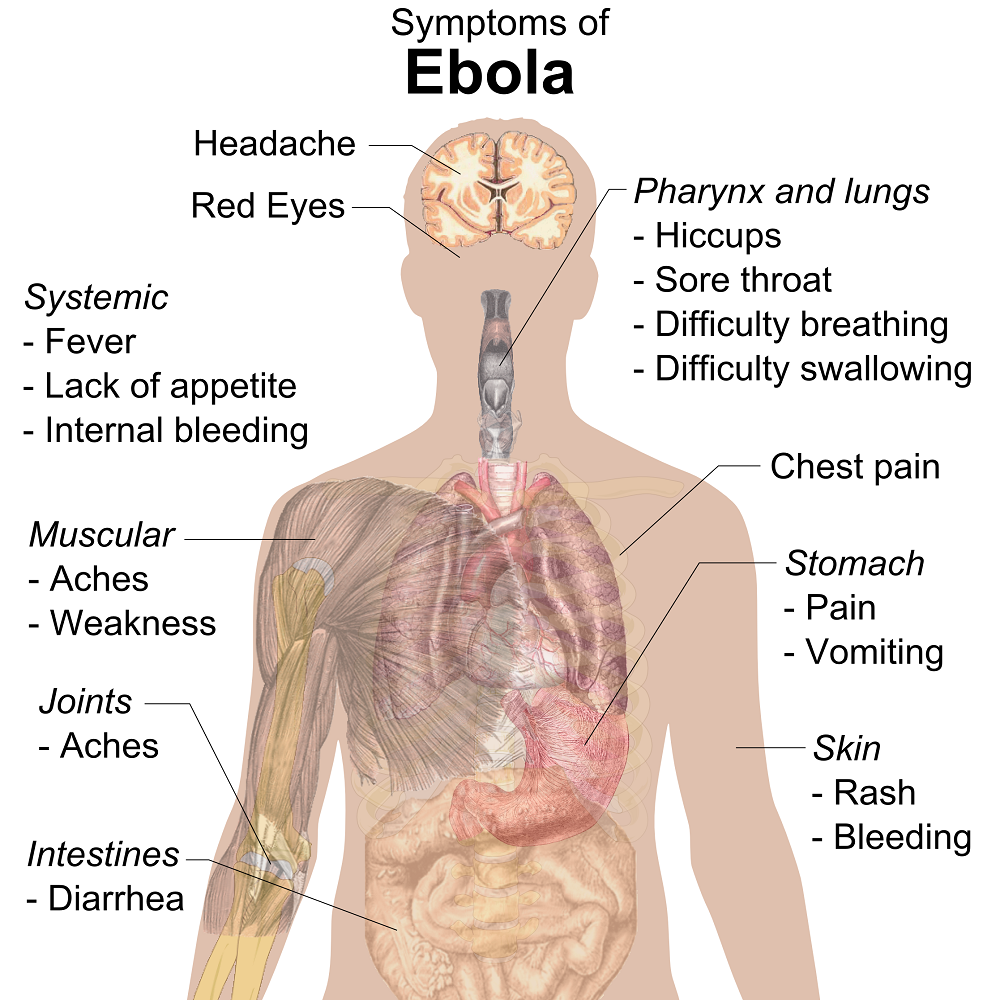
- Acute, serious illness which is often fatal if untreated.
- High fever.
- Joint and muscle aches.
- Sore throat.
- Stomach pain.
- Lack of appetite.
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Rashes
- Symptoms of impaired kidney and liver function in few cases
- Internal and external bleeding such as oozing from the gums, blood in the stools
- Low levels of white blood cell and platelet counts and elevated levels of liver enzymes.
If you do observe these symptoms then do rush to a nearby trauma centre get treated.
Ebola Disease Treatment:
Natural Ebola virus hoots are fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family. The transmission of the virus may take place through blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected animals such as chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, forest antelope and porcupines which are found ill or dead or in the rainforest in to the human body. Later the human to human transmission of the disease starts as with the similar transmission that is through blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people, and with surfaces and materials and coming in to contact with their used articles. The paramedic and health care assistants assisting the affected victims and patients are often found to be infected without following the necessary measures to get prevented from this disease.
It has been observed that in the burial ceremonies where mourners have direct contact with the body of the deceased person can also plays a key role in the transmission of Ebola. As long as blood and body fluids, including semen and breast milk, contain the virus the infected person remain infectious and the men’s who gets recovered from this chronic disease may transmit the virus through their semen for up to 7 weeks after recovery from illness.
Ebola Virus Diagnosis:
Ebola Virus diagnosis can be confirmed with the symptoms and at the same time there may be a disarray to judge whether it is truly Ebola Infection or any other disease like malaria, typhoid fever and meningitis. Thus here are the few diagnosis measures which confirms the infection of Ebola virus.
- Electron microscopy
- Virus isolation by cell culture
- Antigen-capture detection tests
- Antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Serum neutralization test
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay.
Diagnoses of Ebola virus must be practiced in extreme medical safety circumstances thus consult a well-equipped and experienced trauma center.
Ebola Virus Cure and Vaccines:
Ebola virus is curable and has medicines is it is detected in earlier stage thus get diagnosed today if you discover any of the above symptoms within you or your nearby fellow human.
- Survival of the infected person may take place with the supportive care-rehydration with oral or intravenous fluids- and treatment of specific symptoms
- Officially yet there is no proven treatment available for Ebola Virus Disease.
- To improve the survival chances of infected person the range of potential treatments including blood products, immune therapies and drug therapies are currently being evaluated for best results.
- Yet there are no licensed vaccines are available although potential vaccines are undergoing human safety testing.
Ebola Virus Preventions:

The best possible prevention’s for Ebola virus are:
- Applying a package of interventions
- Best case managements of victims and infected patients
- Maintaining Surveillance and contact tracing
- A good laboratory service
- Safe burials of dead bodies
- Safe Social mobilization
- Raising awareness about Ebola Virus and its risk factors with protective measures to reduce human transmission.
- Reduce risk of wildlife-to-human transmission from contact with infected fruit bats or monkeys/apes and the consumption of their raw meat.
- Handling animals with preventive measures such as wearing gloves and other appropriate protective clothing.
- Well-cooked animal products such as meat and other products must be consumed.
- Spread the importance of good hygiene and maintaining a clean environment.
Chronology of previous Ebola virus disease outbreak:
| Year | Country | Ebolavirus species | Cases | Deaths | Case fatality | |
| 2012 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Bundibugyo | 57 | 29 | 51% | |
| 2012 | Uganda | Sudan | 7 | 4 | 57% | |
| 2012 | Uganda | Sudan | 24 | 17 | 71% | |
| 2011 | Uganda | Sudan | 1 | 1 | 100% | |
| 2008 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Zaire | 32 | 14 | 44% | |
| 2007 | Uganda | Bundibugyo | 149 | 37 | 25% | |
| 2007 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Zaire | 264 | 187 | 71% | |
| 2005 | Congo | Zaire | 12 | 10 | 83% | |
| 2004 | Sudan | Sudan | 17 | 7 | 41% | |
| 2003 (Nov-Dec) | Congo | Zaire | 35 | 29 | 83% | |
| 2003 (Jan-Apr) | Congo | Zaire | 143 | 128 | 90% | |
| 2001-2002 | Congo | Zaire | 59 | 44 | 75% | |
| 2001-2002 | Gabon | Zaire | 65 | 53 | 82% | |
| 2000 | Uganda | Sudan | 425 | 224 | 53% | |
| 1996 | South Africa (ex-Gabon) | Zaire | 1 | 1 | 100% | |
| 1996 (Jul-Dec) | Gabon | Zaire | 60 | 45 | 75% | |
| 1996 (Jan-Apr) | Gabon | Zaire | 31 | 21 | 68% | |
| 1995 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Zaire | 315 | 254 | 81% | |
| 1994 | Cote d’Ivoire | Taï Forest | 1 | 0 | 0% | |
| 1994 | Gabon | Zaire | 52 | 31 | 60% | |
| 1979 | Sudan | Sudan | 34 | 22 | 65% | |
| 1977 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Zaire | 1 | 1 | 100% | |
| 1976 | Sudan | Sudan | 284 | 151 | 53% | |
| 1976 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Zaire | 318 | 280 | 88% |
On a concluding note we would like to say that the best part would be to get diagnosed if you sense any symptoms of Ebola Virus disease, stay away from human population if you’re infected or stay away from the infected person and his used articles and body fluids. Have the medication and visit the trauma center so that we are not gonna miss you. Spread the smile and spread the message. Share this post and valuable info with your dear ones and the rest of the world. Stay tuned to All India Round Up for best posts and well versed updates.